Acute Bronchitis
Our related Patient EducationBronchitis is infection and inflammation of bronchi- tubes that carry oxygen in the lungs. Usually bronchitis occurs after a person gets cold or flu and is usually viral infection initially. Antibiotics may not act during this phase. If it gets secondarily infected with bacteria, antibiotics would be required. We will discuss regarding acute bronchitis here. Chronic bronchitis is something that smoker may get.
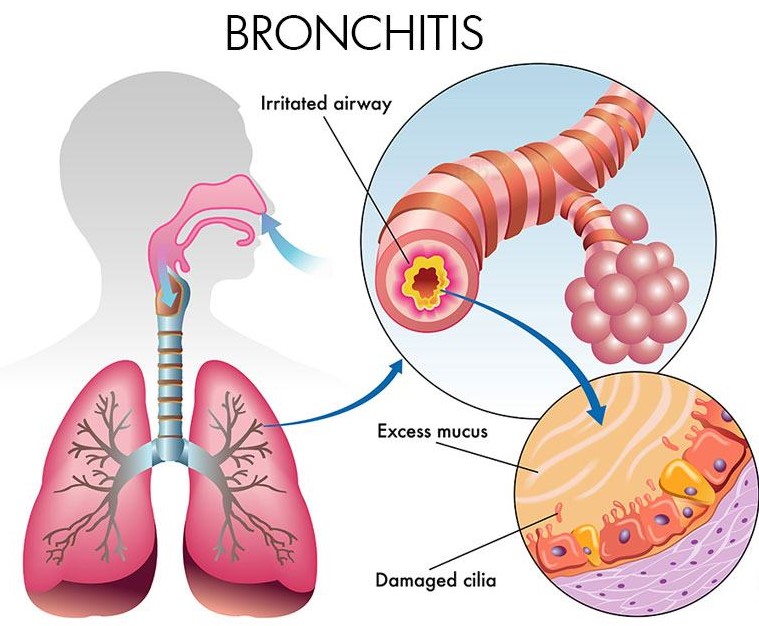
If you have cough more than 14 days associated with
Usually bronchitis does not require any specific tests, however if your symptoms are not improving, doctor may advice you following tests to exclude other differential diagnosis
Chest X-ray
Sputum test for TB and Culture for bacteria
Serum Ig E
CT scan of chest
Bronchitis almost always goes away on its own, although it can take a few weeks. Different treatments you can try include:
Hand hygiene with soap and water Or Hand gel with alcohol in it to clean your hands.

Cover your mouth and nose with your elbow or tissue paper while coughing or sneezing..