Adverse Drug Reactions due to Anti TB Treatment
What are the adverse drug reactions which may occur due to anti-TB treatment?
Anti-TB treatment is given for at least 6 months for drug-sensitive tuberculosis and may extend up to 18–20 months for multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis.

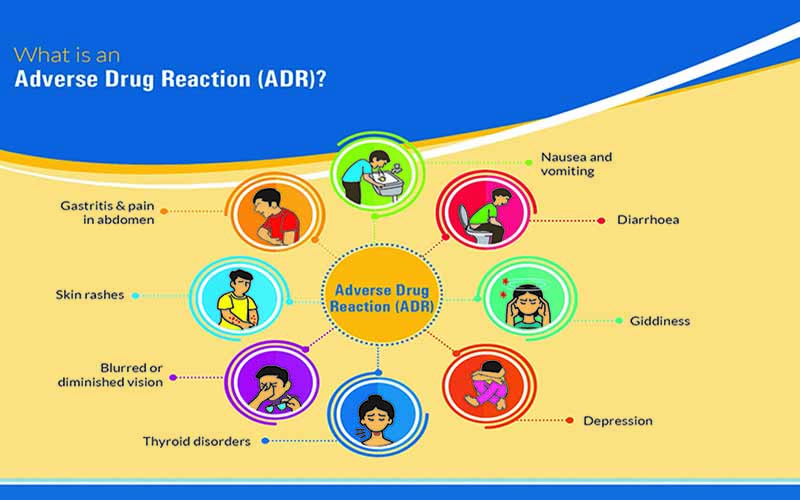
Some of the common adverse drug reactions are as follows:
- Gastritis and abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Skin rashes
- Giddiness
- Pins and needle sensation in hands and feet (tingling / numbness)
- Skin rashes and/or tanning of skin
- Depression
- Hypothyroidism
- Blurred vision
- Palpitations
What tests or work-up may be required in case of adverse drug reactions due to ATT?
- Complete blood counts (CBC)
- Liver function tests (LFT)
- Renal function tests (RFT)
- Thyroid function evaluation
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Nerve conduction study (NCV)
- Fundoscopy and color vision testing (eye evaluation)
- Audiometry (ENT evaluation)
- Psychiatric evaluation
How to manage these adverse drug reactions?
- Visit your doctor if you experience any adverse effects
- Do not stop anti-TB medicines on your own
- Your doctor may prescribe medicines to reduce adverse effects
- Some anti-TB medicines may be taken with food, at specific time intervals, or at a reduced dose to avoid or minimize adverse effects
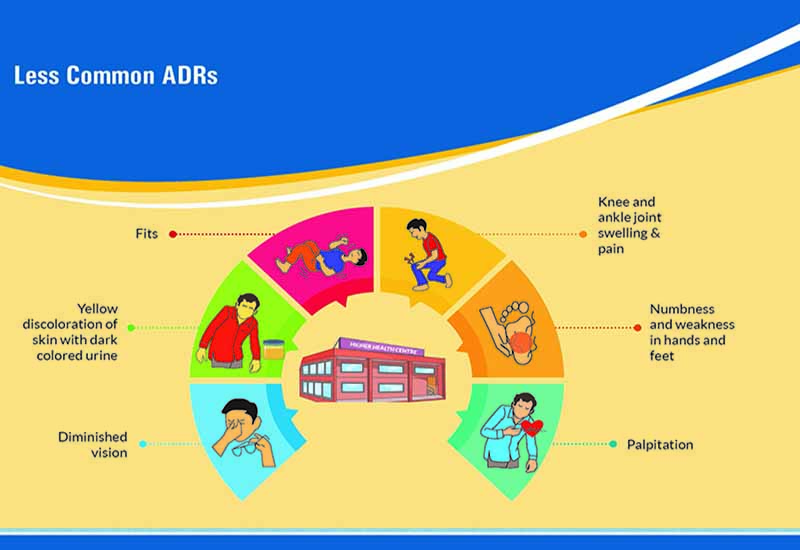
Which are the side effects that require immediate attention to higher center?
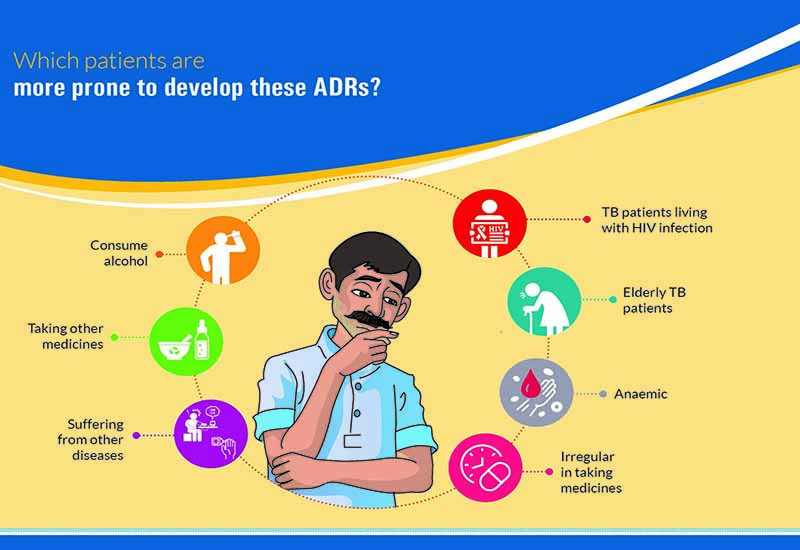
Which patients are more prone to develop to develop these ADRs?
- Patients who consume alcohol
- Patients with TB and HIV co-infection
- Elderly TB patients
- Anemic patients
- Patients taking medicines irregularly
- Patients suffering from other medical illnesses
- Patients taking other medications
Consult your doctor to avoid drug interactions if you are taking other medicines.
Source: www.tbcindia.gov.in
Dr. Sagar Raiya's Publications
See Our all publications and presentations
